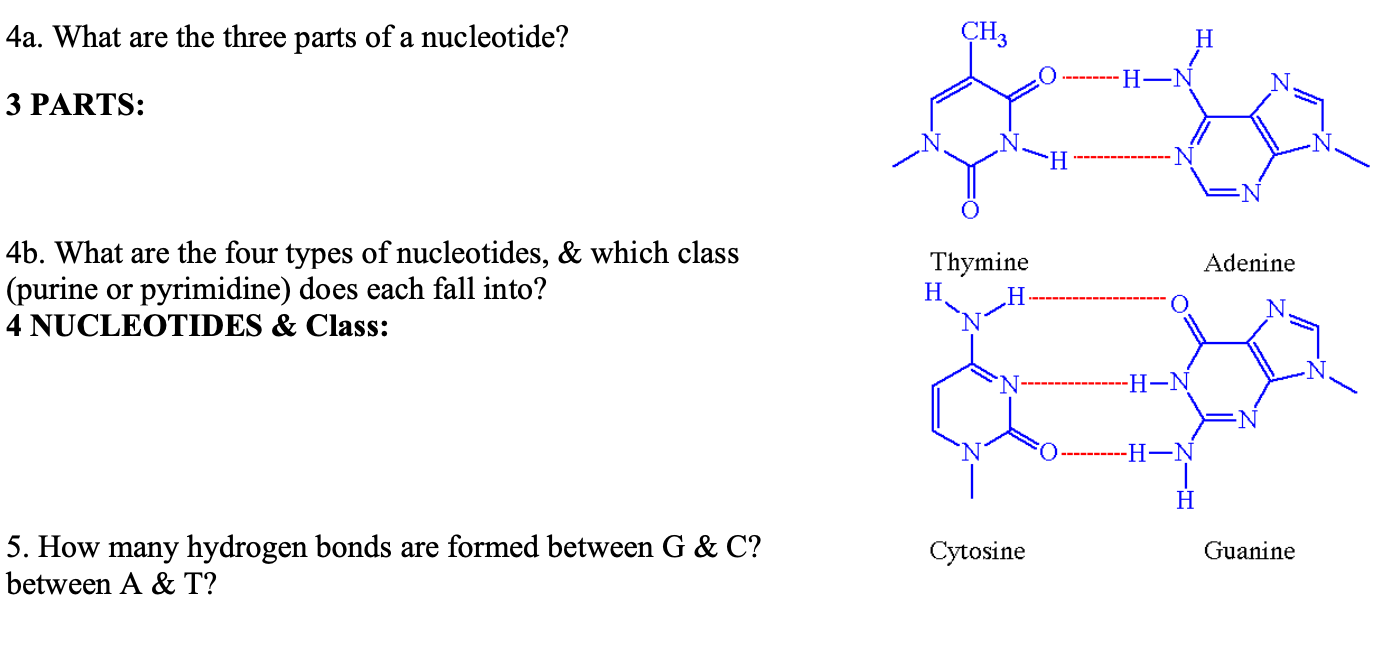
42 what are the three parts in a nucleotide
Ribosomal RNA - Wikipedia WebRibosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form small and large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the … Join LiveJournal WebPassword requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;
Nucleotide - National Human Genome Research Institute
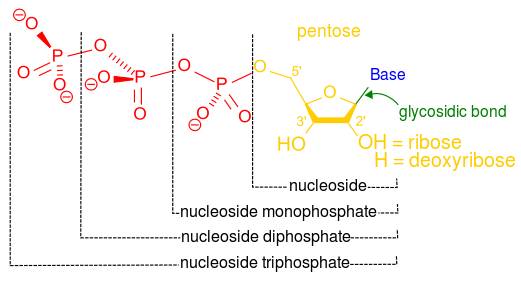
What are the three parts in a nucleotide
Transfer RNA - Wikipedia WebTransfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins. tRNAs genes from Bacteria are typically shorter (mean = 77.6 bp) than tRNAs … › createJoin LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols; Primer designing tool - National Center for Biotechnology … WebFor example, entering "50 100" would mean that the left or the right primers must span the junction between nucleotide position 50 and 51 or the junction between position 100 and 101 (counting from 5' to 3'). You can also specify in the fields below the minimal number of nucleotides that the left or the right primer must have on either side of the junctions. This …
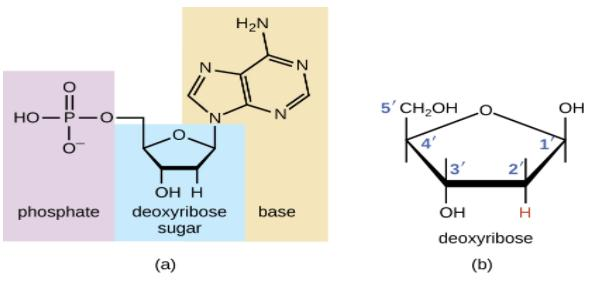
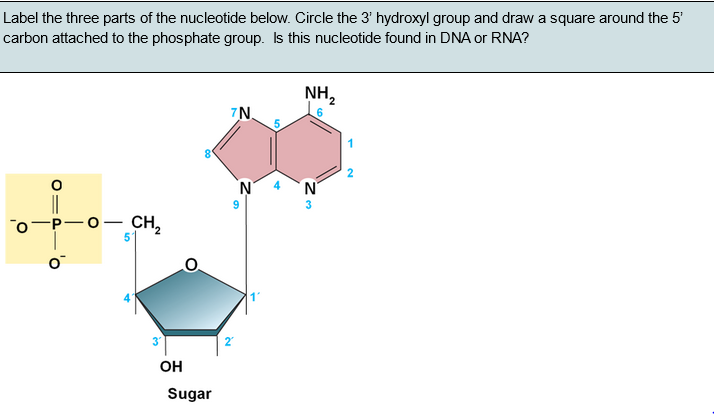
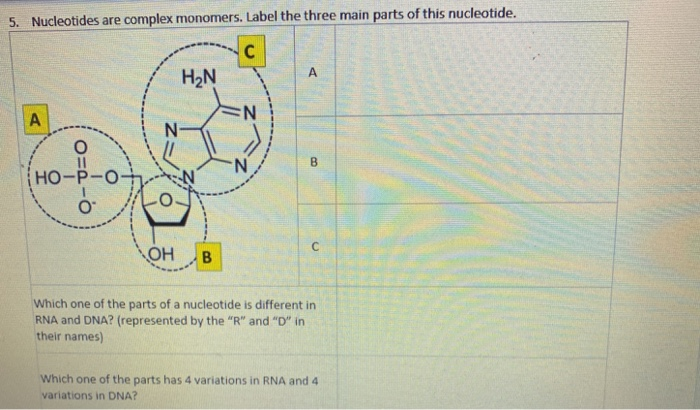
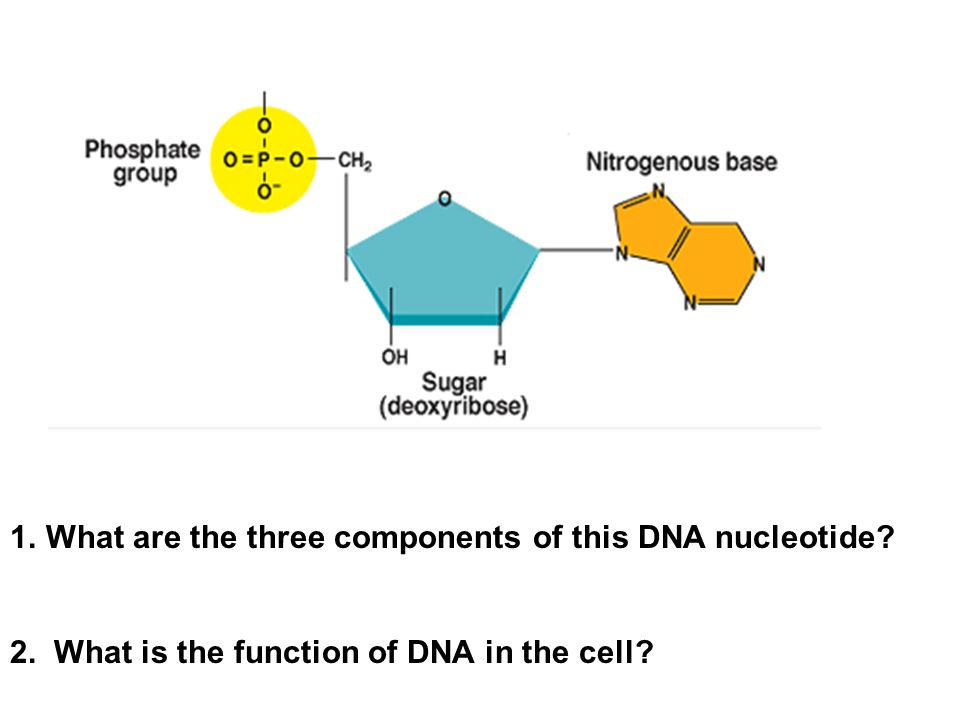
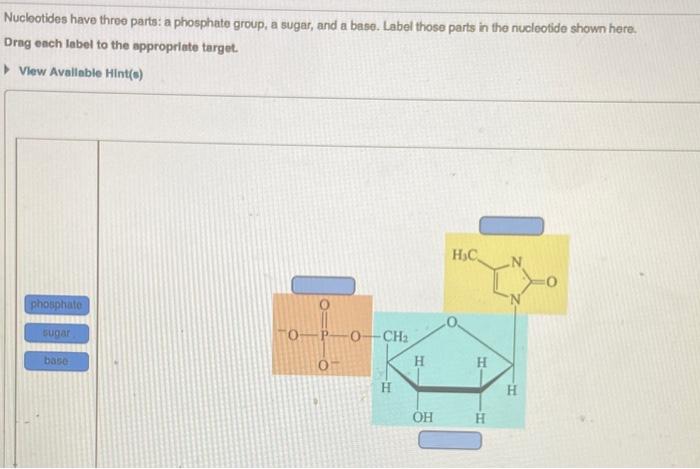
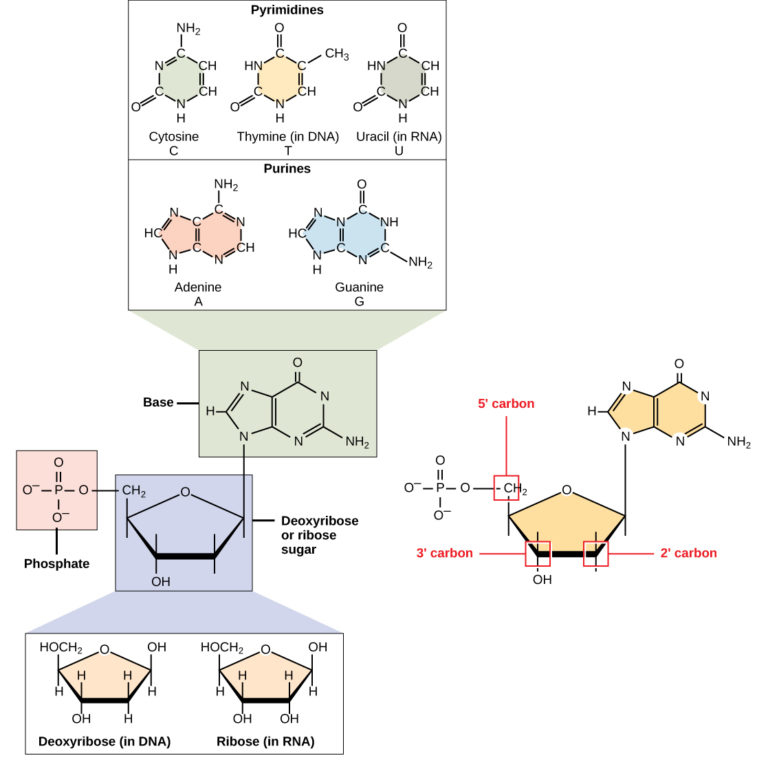
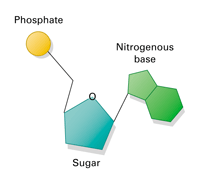
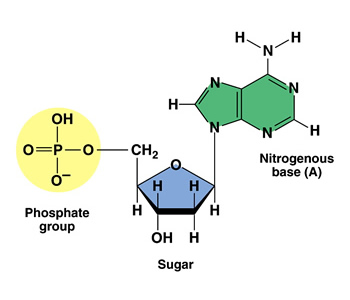
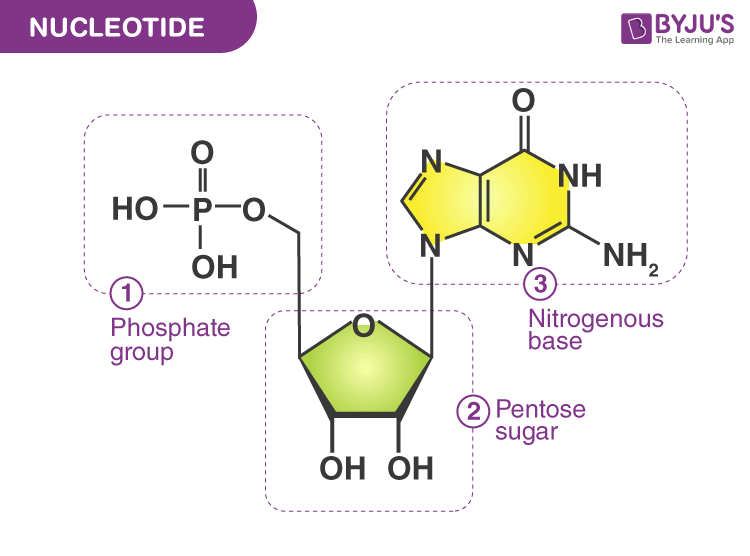
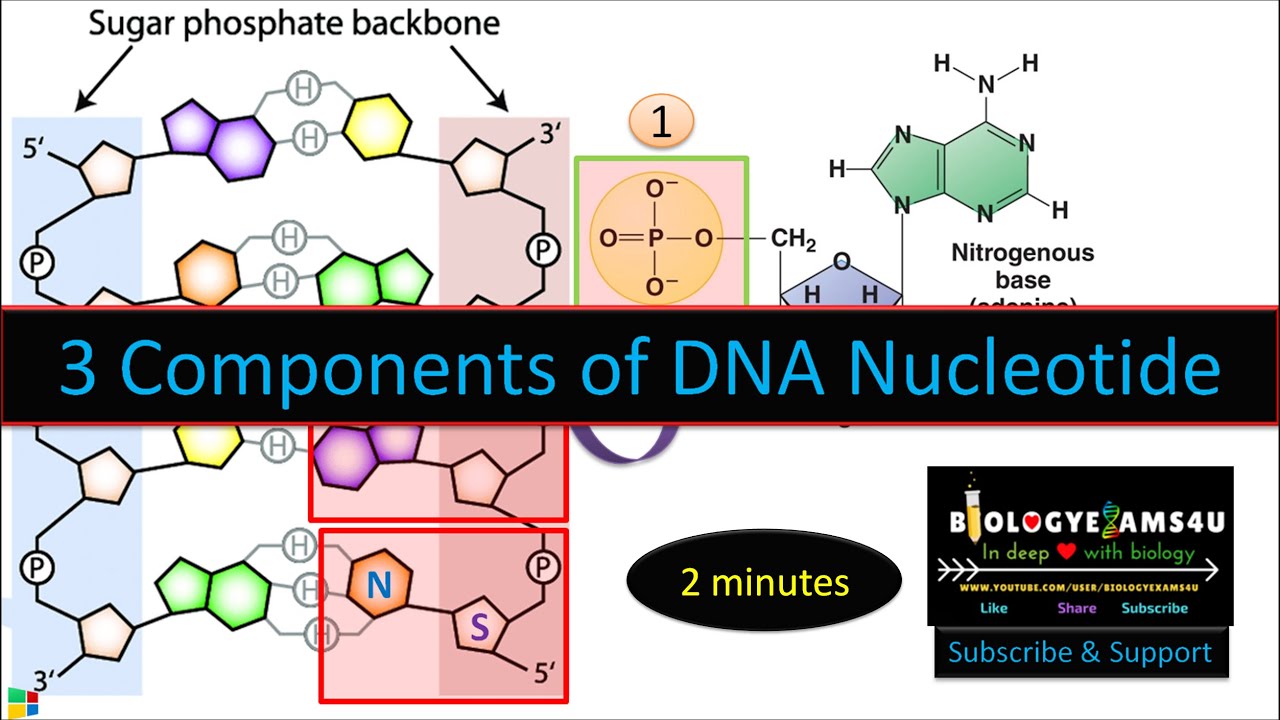
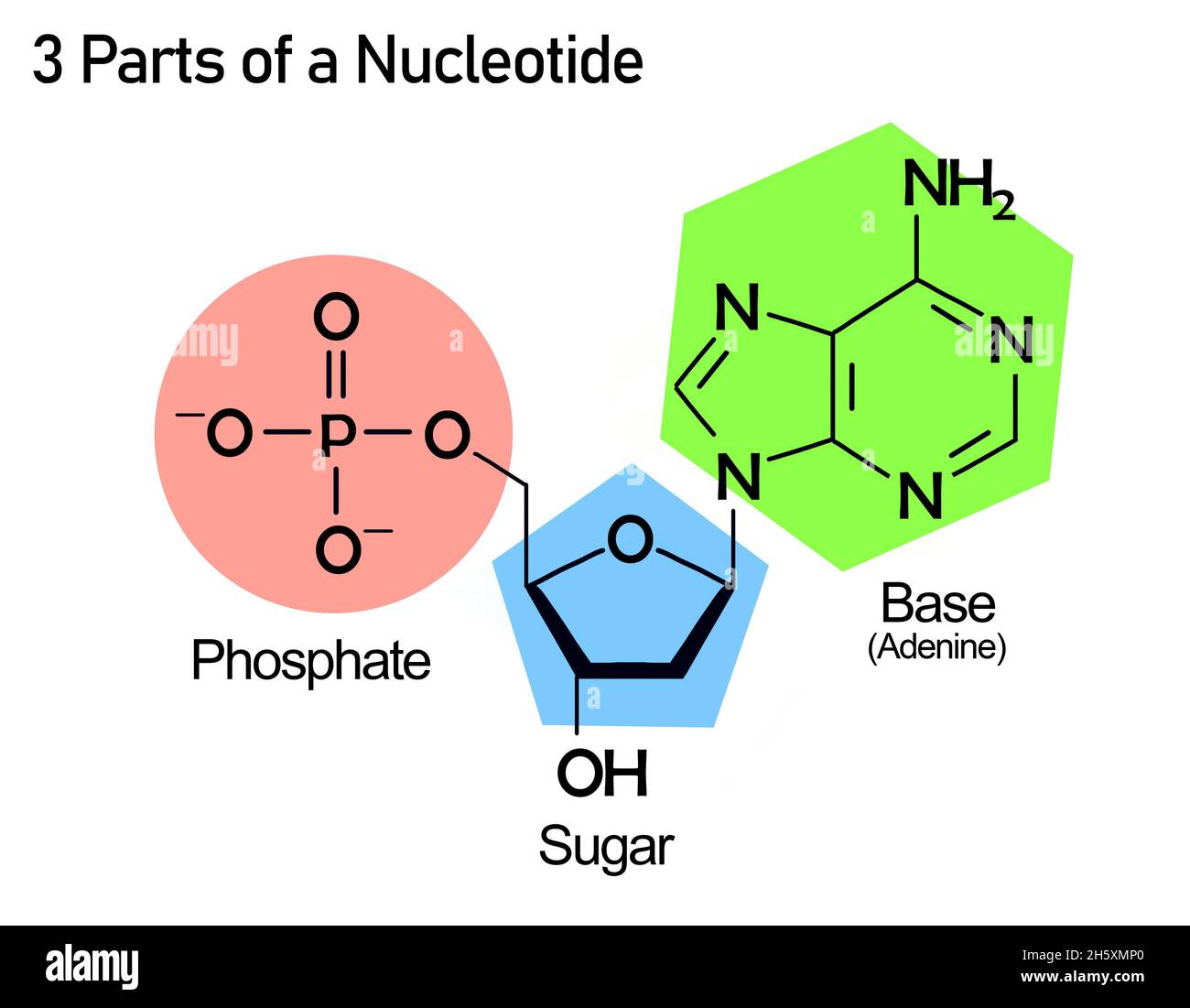
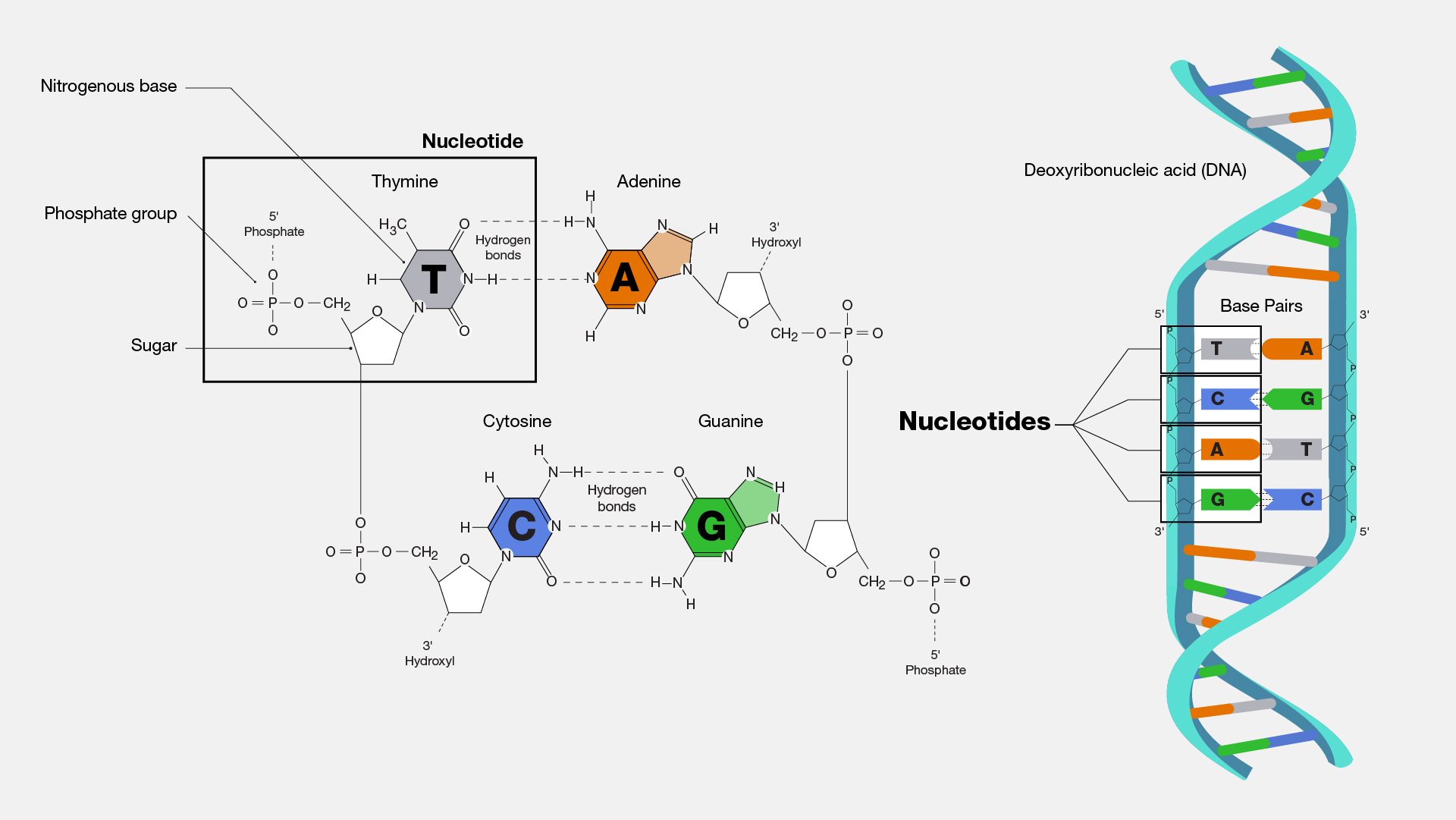
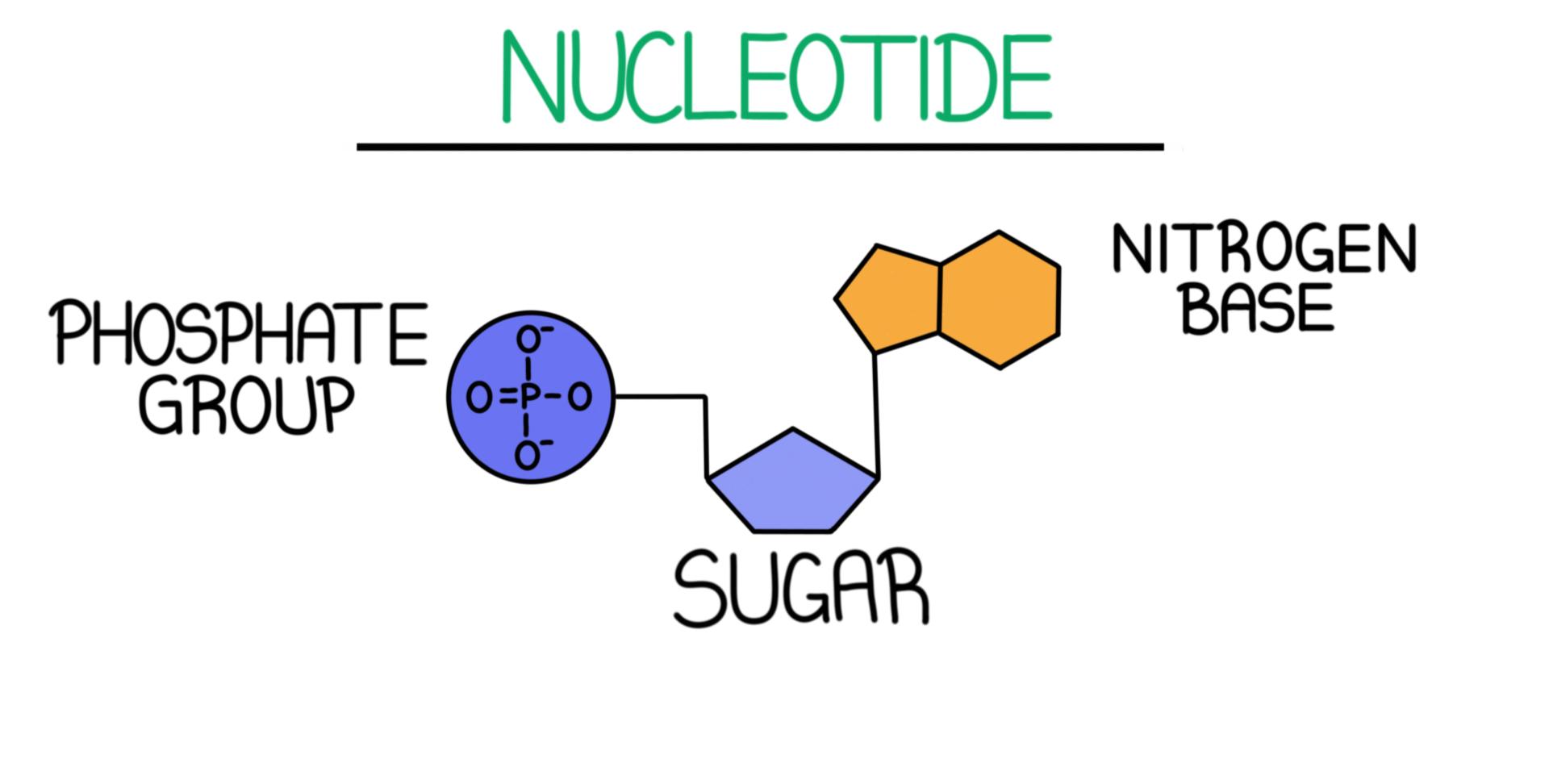
What are the three parts in a nucleotide. PHSchool.com Retirement–Prentice Hall–Savvas Learning Company WebPHSchool.com was retired due to Adobe’s decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support. 3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected - ThoughtCo Web24/01/2020 · A free nucleotide may have one, two, or three phosphate groups attached as a chain to the 5-carbon of the sugar. When nucleotides connect to form DNA or RNA, the phosphate of one nucleotide attaches via a phosphodiester bond to the 3-carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone of the nucleic acid . Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function Web04/10/2019 · A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. RNA contains uracil, instead of thymine. A nucleotide within a chain makes up the genetic material of all known living things. They also serve a number of function ... › blog › what-are-the-three-parts-of-aWhat are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io Mar 01, 2022 · The assembly of nucleotides (1) differentiates them from nucleosides, which do not contain a phosphate group (in the blue box); (2) allows the nucleotide to connect to other nucleotides when the nitrogenous base forms a hydrogen bond with another nucleotide’s nitrogenous base; as well as (3) allows the phosphate to form a phosphodiester bond ...
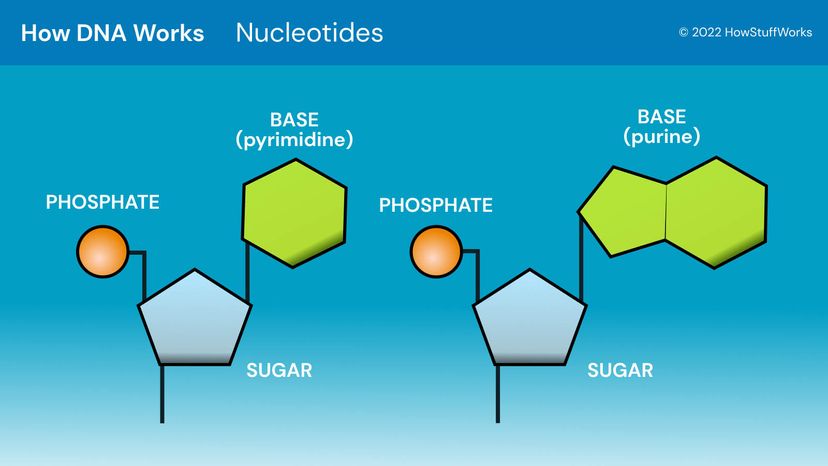
ppubs.uspto.gov › pubwebapp › staticPatent Public Search | USPTO Welcome to Patent Public Search. The Patent Public Search tool is a new web-based patent search application that will replace internal legacy search tools PubEast and PubWest and external legacy search tools PatFT and AppFT. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › NucleotideNucleotide - Wikipedia Structural elements of three nucleotides—where one-, two- or three-phosphates are attached to the nucleoside (in yellow, blue, green) at center: 1st, the nucleotide termed as a nucleoside monophosphate is formed by adding a phosphate (in red); 2nd, adding a second phosphate forms a nucleoside diphosphate; 3rd, adding a third phosphate results ... Nucleotide - Wikipedia WebA nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase (the two of which together are called a nucleoside), and one phosphate group.With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleoside monophosphate", "nucleoside diphosphate" or "nucleoside triphosphate", depending on … biologydictionary.net › nucleotideNucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function Oct 29, 2016 · A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.
Google Scholar Citations WebGoogle Scholar Citations lets you track citations to your publications over time. Gene expression - Wikipedia WebGene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect.These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA … scholar.google.com › citationsGoogle Scholar Citations Google Scholar Citations lets you track citations to your publications over time. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Cell_(biology)Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Cell types. Cells are of two types: eukaryotic, which contain a nucleus, and prokaryotic cells, which do not have a nucleus, but a nucleoid region is still present.. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms, while eukaryotes may be either single-celled or mult
Primer designing tool - National Center for Biotechnology … WebFor example, entering "50 100" would mean that the left or the right primers must span the junction between nucleotide position 50 and 51 or the junction between position 100 and 101 (counting from 5' to 3'). You can also specify in the fields below the minimal number of nucleotides that the left or the right primer must have on either side of the junctions. This …
› createJoin LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;
Transfer RNA - Wikipedia WebTransfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins. tRNAs genes from Bacteria are typically shorter (mean = 77.6 bp) than tRNAs …

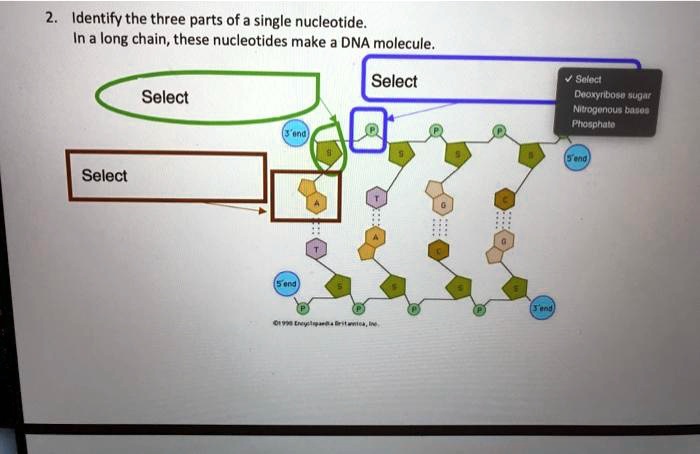
What does DNA mean?, DNA is made of repeating units called nucleotides. What are the, three parts of a nucleotide?, If a particular DNA molecule contained 20 per cent thymine, how, much of the ...






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)












Post a Comment for "42 what are the three parts in a nucleotide"